
Future of Agriculture: IoT, Robotics, and Precision Farming Revolutionizing Food Production
The world's population is projected to reach a staggering 9.7 billion by 2050. This rapid increase in population is causing a lot of strain on our food production systems. Our current agricultural practices are struggling to keep pace with this demand as they face multiple challenges. The combination of population growth, resource depletion, climate change, and labor shortages creates a perfect storm for a potential food crisis.
To ensure food security for the future, a significant transformation in agriculture is essential. This transformation requires a shift towards sustainable, resource-efficient practices that can meet the growing demand without jeopardizing our environment or the livelihoods of farmers. This is where the exciting world of technology steps in.
Advancements in IoT, robotics, and precision farming offer a powerful solution to the challenges faced by agriculture. These innovations can optimize resource use, maximize yields, and pave the way for a more sustainable and productive future for food production.
The Looming Challenge: Feeding a Growing Population
For millennia, agriculture has sustained humanity. However, traditional farming methods face significant challenges in the 21st century. Climate change disrupts weather patterns and reduces arable land. Water scarcity threatens irrigation, and resource depletion raises concerns about long-term sustainability.
The need for increased food production goes hand-in-hand with the need for responsible resource management. This is when technology works its magic.
The Rise of the Tech-Savvy Farmer: IoT and Precision Farming
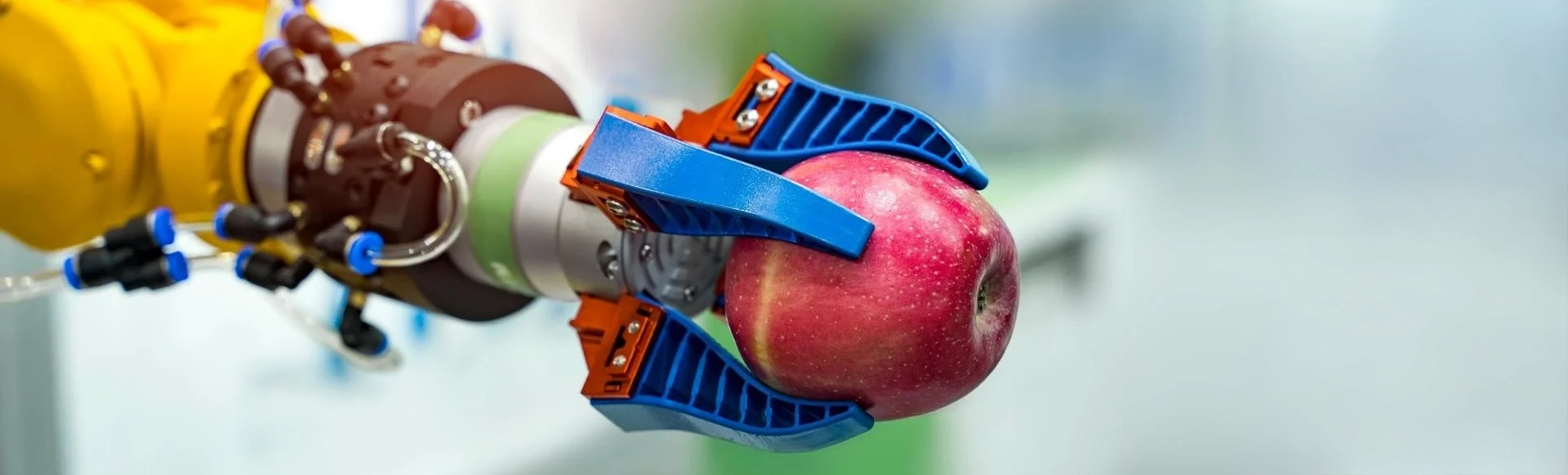
Precision farming utilizes a data-driven approach to optimize resource use and crop yields. It leverages a network of interconnected devices (the IoT) that collect real-time data on various aspects of the farm environment, including:
Soil moisture levels: Sensors monitor soil moisture, enabling farmers to irrigate precisely when and where needed, minimizing water waste.
Nutrient levels: Sensors assess soil nutrient content, allowing for targeted fertilizer application, and reducing excess use and environmental pollution.
Crop health: Drones equipped with multispectral imaging can detect diseases or pest infestations in their early stages, enabling timely interventions with minimal chemical use.
Weather data: Weather stations provide real-time weather forecasts, allowing farmers to plan their activities and mitigate potential risks from extreme weather events.
This data is then analyzed by advanced software and translated into actionable insights. Farmers can use these insights to:
Optimize irrigation: By understanding moisture levels and weather forecasts, farmers can adjust irrigation schedules to provide the right amount of water at the right time.
Improve fertilizer use: Knowing the exact nutrient profile of the soil allows for targeted fertilizer application, increasing crop yields and minimizing environmental impact.
Enhance disease and pest control: Early detection through drones and sensors minimizes damage caused by pests and diseases. Targeted interventions with minimal chemicals promote sustainable practices.
Predict crop yields: Data analysis helps predict crop yields with greater accuracy, allowing farmers to plan effectively for harvesting, storage, and market needs.
The Robots are Coming! : Robotics in Agriculture
Robotics is no longer science fiction. Advanced robots are making their way into fields, performing various tasks with efficiency and precision. Here are some ways robots are transforming agriculture:
Automated planting and harvesting: Robots can precisely plant seeds at optimal depths and spacings, ensuring consistent growth patterns. They can also harvest crops with greater efficiency and reduced labor costs.
Weed control: Autonomous robots equipped with weed-killing lasers or mechanical tools can eliminate unwanted plants without harming crops, minimizing herbicide use.
Livestock management: Robotic milking machines can automate milking processes, reducing stress on animals and improving milk quality. Additionally, robots can deliver feed and monitor animal health.
Field monitoring: Ground and aerial robots can continuously monitor field conditions, providing valuable data on crop health and potential issues
These robotic applications offer numerous benefits:
Increased productivity: Robots can work tirelessly, covering larger areas and completing tasks faster than human workers.
Reduced labor costs: Automation can alleviate the pressure on the shrinking agricultural workforce and reduce reliance on manual labor.
Improved efficiency and precision: Robots can perform tasks with greater accuracy and consistency than manual labor, minimizing waste and maximizing yields.
Reduced environmental impact: By enabling targeted resource use and minimizing chemical application, robots contribute to sustainable farming practices.
The Connected Farm: Benefits and Challenges
The integration of IoT and robotics promises significant benefits for the future of agriculture. However, there are a few obstacles that we need to tackle:
Cost of technology: Implementing these technologies can be expensive for smaller farms. Government initiatives and industry collaboration can play a role in making them more accessible through subsidies, tax breaks, or financing options.
Data security: Protecting the vast amount of data collected by IoT devices is crucial. Cybersecurity measures need to be implemented to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data privacy. Robust encryption and access control protocols are essential to safeguard sensitive farm data.
Digital divide: Rural regions may lack the infrastructure required for seamless data transmission and integration, potentially creating a digital divide between different farms. Investments in rural broadband infrastructure are necessary to bridge the gap and ensure equitable access to these technologies.
Final Thoughts
The future of agriculture is brimming with possibilities thanks to advancements in IoT, robotics, and precision farming. By embracing these technologies, farmers can become more efficient, productive, and sustainable. However, addressing challenges like affordability, data security, and equitable access will be crucial to ensure these innovations benefit all stakeholders in the agricultural sector.