
The Power of Virtual Reality for Crisis Response and Emergency Training
Emergencies can arise at any moment, from natural disasters like earthquakes and floods to human-made crises such as terrorist attacks or industrial accidents. In such scenarios, the difference between a successful response and a catastrophic failure often hinges on the quality of training received beforehand. Traditional emergency training methods, while beneficial, often need to catch up in several areas.
Virtual reality (VR) in emergency training is a powerful tool that not only enhances traditional training methodologies but also prepares individuals and organizations for real-world emergencies more effectively. It has become this new addition to the tabletop exercises that either replaces or complements the current traditional approaches to disaster preparedness training.
How Virtual Reality is Transforming Emergency Training

1. Enhanced Realism and Immersion
One of the most significant advantages of using virtual reality in emergency training is the unparalleled level of realism and immersion it provides. Trainees can engage with lifelike environments, ranging from a burning building to a chaotic disaster scene, all designed to evoke genuine emotional responses. This immersive experience allows individuals to practice their skills in a safe yet realistic setting, preparing them for the intense stress and pressure they may face in actual emergencies.
2. Repeated Practice in Diverse Scenarios
VR training allows users to practice their skills repeatedly in various scenarios, which can be tailored to specific training needs. Emergency responders can experience multiple situations—from managing a mass casualty incident to responding to an active shooter event—without the constraints of time or resources. This repeated exposure not only reinforces learning but also helps build muscle memory, enabling quick and effective responses during real crises.
3. Safe Learning Environment
One of the most compelling aspects of virtual reality in emergency training is the ability to create a safe learning environment. Trainees can make mistakes, learn from them, and refine their responses without the risk of harming themselves or others. This safe space encourages experimentation and fosters confidence, allowing individuals to develop their skills more effectively.
4. Real-time Feedback and Analytics
Many VR training systems come equipped with real-time feedback and performance analytics. This feature enables trainers to monitor each participant's performance, providing insights into areas that require improvement. By analyzing the data collected during VR training sessions, organizations can customize training programs to address specific weaknesses, ensuring that all team members are adequately prepared for emergencies.
5. Cost and Time Efficiency
While the initial investment in virtual reality technology can be significant, the long-term cost savings associated with VR training are noteworthy. Organizations can reduce expenses related to physical training environments, materials, and logistics. Furthermore, VR training can be conducted remotely, saving valuable time and resources that would otherwise be spent on travel and accommodations for training sessions.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Emergency Training

1. Firefighting Training
Virtual reality is being increasingly utilized in firefighting training. Firefighters can experience various fire scenarios, including residential fires, industrial blazes, and wildfires. By immersing trainees in these situations, they can practice decision-making, risk assessment, and emergency response techniques in a controlled environment. This training is invaluable, as it prepares them for the unpredictable nature of real-life firefighting.
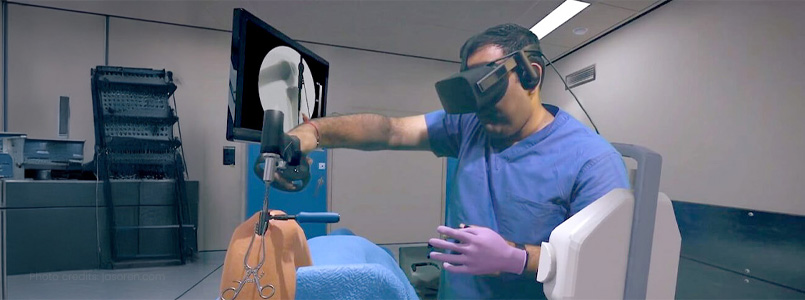
2. Medical Emergency Response
In the field of healthcare, VR is transforming the way medical professionals prepare for emergency situations. Medical personnel can practice trauma care, triage, and patient management in lifelike scenarios. For instance, they can simulate responding to a mass casualty event or managing a patient suffering from a heart attack. This hands-on experience is critical for building confidence and competence in high-pressure medical emergencies.

3. Law Enforcement and Active Shooter Drills
Virtual reality is revolutionizing law enforcement training, especially in preparing for active shooter incidents. Officers can practice responding to various active shooter scenarios, enhancing their decision-making and tactical skills. The immersive nature of VR allows them to navigate complex environments, coordinate with team members, and assess threats in real-time. This type of training fosters better situational awareness and prepares officers to respond effectively in real emergencies.

4. Disaster Management Training
Emergency managers can utilize VR simulations to prepare for various disaster scenarios, from natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes to public health emergencies. By participating in these simulations, they can practice coordinating responses, managing resources, and leading teams during crises. The insights gained from VR training can significantly improve their preparedness and effectiveness in real-world situations.

5. Corporate Emergency Preparedness
Businesses are also recognizing the value of virtual reality in emergency training. Companies can use VR to train employees on emergency procedures, evacuation plans, and safety protocols. This training can be tailored to specific industries, ensuring that employees are well-prepared to respond to emergencies that may arise in their workplaces. Furthermore, VR training can enhance employee engagement and retention of critical safety information.
Successful Implementation of VR in Emergency Training
1. Firefighter Training
Fire departments around the world have begun integrating VR into their training programs. For example, the Phoenix Fire Department in Arizona has utilized VR technology to create immersive training scenarios that replicate the chaos and unpredictability of a real fire. Trainees can practice navigating through smoke-filled rooms, conducting rescues, and extinguishing fires—all within a safe virtual environment. This innovative approach has led to improved response times and better overall performance during actual emergencies.
2. Medical Emergency Response
Virtual reality has also found its place in medical emergency training. Organizations like the University of Maryland Medical Center have implemented VR simulations to train healthcare providers in critical care situations. Trainees can practice performing life-saving procedures, such as intubation or administering medication, in a realistic environment. The ability to repeat scenarios until proficiency is achieved enhances skill retention and prepares medical professionals for high-pressure situations.
3. Law Enforcement Training
Law enforcement agencies have adopted VR technology to enhance their training programs as well. The use of VR simulations allows officers to practice de-escalation techniques, decision-making under stress, and responding to active shooter situations. By immersing officers in realistic scenarios, they can develop the skills necessary to handle critical incidents effectively. The Miami-Dade Police Department, for example, has reported improved decision-making and reduced use-of-force incidents after VR training into its curriculum.
Challenges of Virtual Reality in Emergency Training
While the potential of virtual reality in emergency training is immense, several challenges and considerations must be addressed:
1. Technology Accessibility
The cost of VR equipment can be a barrier for some organizations, particularly smaller agencies or businesses. Ensuring that VR training is accessible to a broad range of emergency responders and organizations is crucial for maximizing its impact.
2. Standardization of Training Protocols
As the use of VR in emergency training grows, establishing standardized protocols and best practices is essential. This standardization will help ensure consistency in training experiences and outcomes across different organizations and sectors.
3. Training Integration
Integrating VR training into existing emergency response training programs can pose challenges. Organizations must determine how to best incorporate VR into their current training curriculum while maintaining continuity and effectiveness.
4. Technology Adaptation
Some individuals may be hesitant to embrace new technology, particularly those who are accustomed to traditional training methods. Organizations must provide adequate support and training for users to ensure they feel comfortable and confident using VR systems.
Final Thoughts
Virtual reality in emergency training is a paradigm shift in how we prepare for crises. By providing realistic, immersive experiences, VR technology enhances learning outcomes, fosters collaboration, and ultimately improves emergency response capabilities. While challenges remain, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, making VR an invaluable tool in the ever-evolving landscape of emergency preparedness.
As organizations continue to explore the possibilities of virtual reality, it is clear that this technology will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of emergency training, ensuring that responders are well-equipped to handle whatever challenges lie ahead. In a world where preparedness can mean the difference between life and death, investing in innovative training solutions like VR is not just an option—it is a necessity.